System Type, Climate and Grid
Page System Type, Climate and Grid
Climate data allows you to determine the climate values to calculate the annual energy yield of the solar system.
The climate data record can be easily selected via the lists for the countries and locations.
Clicking the  Select opens the Meteosyn climate data selection, structured according to the countries of the world.
Select opens the Meteosyn climate data selection, structured according to the countries of the world.
Postal codes, latitude, longitude and time zone help you to find the right data record.
Choose (or generate) a climate data record as close as possible to your project location.
Depending on the selected country typical presettings such as load imbalance or tariffs are set automatically.
MeteoSyn has its own help function which you can access directly in MeteoSyn.
 The selected climate data record can be saved as default.
The selected climate data record can be saved as default.
Simulation Parameters
Enter the following settings:
Losses due to deviation from standard spectrum AM 1.5:
Spectral mismatch changes the module’s characteristic curve, which is measured against a standard spectrum. In Central Europe a correction factor of an annual average of 1% can be allowed for. The correction factor should be entered in the field provided.
- Calculate the irradiance with synthesized minute values
Before the simulation, irradiance in minute values is synthesized from the hourly values. This provides more accurate simulation results. The use of minute values is especially important in inverter sizing factors of more than 110% or with inverter limitation.
The synthesis of the minute values is performed only once per site.
The properties of the AC network are also set here. These are:
- The Grid Voltage between phase and neutral: in 1- or 3-phase networks; typically 230 V.
In the case of two-phase systems with 120V, a split-phase topology is assumed, i.e., the two phases, L1 and L2 are phase shifted by 180 degrees between each other and so have 240V voltage difference.
- The number of phases that make up the AC mains.
Small systems are generally operated on a single phase, and larger systems on three-phases. In North America, two-phase topologies (including split phase or single-phase three-wire type networks) are also used.
- Reactive power
Enter a displacement factor cos(φ) between 0.8 und 1.
With a cos(φ) < 1, the useable active power of the inverter will be less.
With a cos φ of 0.95, only 95% of the inverter apparent power can be used as active power. The inverter should therefore be sized 5 % larger.
If the inverter is sized too small, the simulation will reveal drops in yield.
- Activate the
 Feed-in-Limitation of the Maximum Feed-in Power, and enter a value in percentage of the installed PV power.
Feed-in-Limitation of the Maximum Feed-in Power, and enter a value in percentage of the installed PV power.
Example: With an installed PV power of 5kWp and a limitation to 70%, the inverter output power on the AC side would be limited to 3.5 kW.
Additionally, you can choose whether limitation is to take place on the inverter or at the feed-in point.
-> for further detail on limitation vs. own use see: Glossary > Inverter output power (AC), limitation to 70% (60%)
- Enter the specific avoided carbon dioxide emissions due to used PV energy in g/kWh. In the project presentation, the avoided CO2is given in grams.
You can change the standard values, e.g. the mains voltage so that it always has this value in newly created projects.
Only available in PV*SOL® premium!

 Use 3D Design
Use 3D Design
The system design with 3D design offers: 3D objects, (roof) area coverage, installation, module and inverter configuration, and cable design
The pages PV module and Inverter no longer apply, as their functions are included in the 3D design.
! A switch from the direct input to 3D discards the design in the direct input.
|
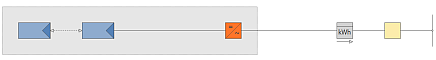
|
|

|
|
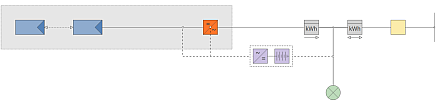
|
|

|
|
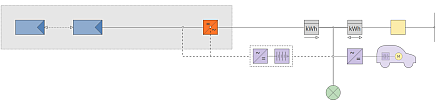
|
|
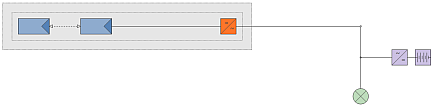
|
Stand-alone PV installations with auxiliary generator (SMA system)
->The page  Consumption, Auxiliary generator, Consumption, Auxiliary generator, .png) Battery inverter and Battery, as well as a modified economic feasibility will be activated. Battery inverter and Battery, as well as a modified economic feasibility will be activated. |
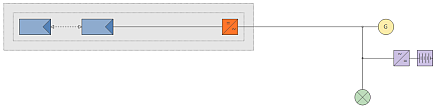
|
-> See also:
Messages


 Climate data
Climate data Select opens the Meteosyn climate data selection, structured according to the countries of the world.
Select opens the Meteosyn climate data selection, structured according to the countries of the world.  The selected climate data record can be saved as default.
The selected climate data record can be saved as default. AC Mains/ Grid
AC Mains/ Grid Feed-in-Limitation of the Maximum Feed-in Power, and enter a value in percentage of the installed PV power.
Feed-in-Limitation of the Maximum Feed-in Power, and enter a value in percentage of the installed PV power. 
 Use 3D Design
Use 3D Design